For ten years ZAutomation has been working on custom projects based on RFID technologies.
Such technologies allow to increase the quality of the processes and to diminish appreciably the errors; the industrial field represents one of the scenarios with greater development, in fact they come predisposed in order to govern the inner processes of production, warehouse and shipment.
By adopting a radio frequency identification system, the quality of processes can be increased for the same number of human resources employed.
RFID TECHNOLOGIES IN LOGISTICS
RFID technology can be applied in logistics as it allows a complete approach to the logics of warehouse and shipment, tracing in automatic the displacements through the installation of reader, or through the access to the information contained in the database.
In our days is more and more recurrent the desire to shorten the times of production and shipment, just for this reason RFID is applied in the production phases, going therefore to reduce the errors in the times of control of the deliveries and payment to warehouse.
RFID is fundamental in the mapping of the warehouse, speeding up the search and retrieval of goods: in a traditional picking system, the operation is slow and risky, as it is based on the operator’s historical memory; with RFID, on the other hand, the system manages and knows the exact location of the goods in the warehouse, generating a speeded-up process with secure and error-free information transfer.
Among the technological features taken up for logistics purposes, chips with increased performance and memory capacity stand out in the UHF area. We have possibilities to design and realise custom rfid, antennas, coatings and tags/transponders even with less sensitivity to the physical environment, i.e. liquids and metals, and spatial orientation.
Less sensitivity to the environment and greater reading accuracy means, in practical terms, avoiding ‘false positives’, i.e. unwanted readings, which are to be considered as error.
Rely on someone who has been offering RFID consulting for years, and choose the best solution for your company.
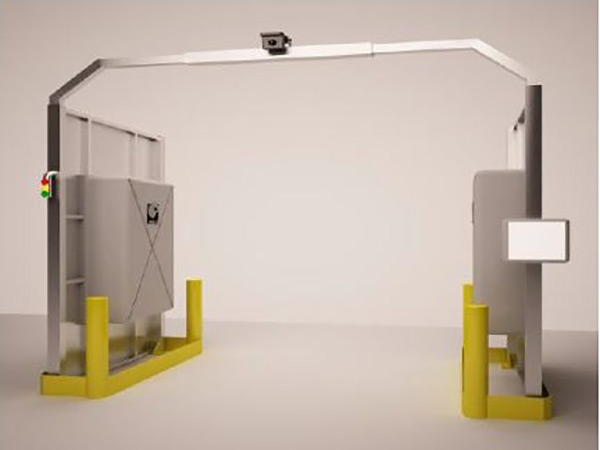
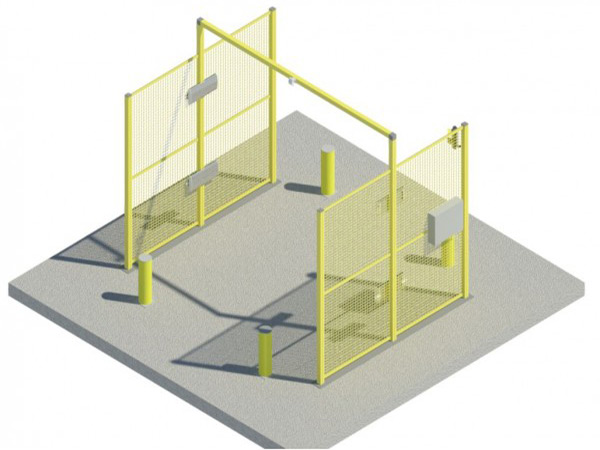
RFID ACCESSES AND GATES
With RFID technology it is possible to design and equip gates with UHF readers, to be used in industrial environments and warehouses close to loading bays, for the automatic identification management of inbound and outbound logistic procedures.
It is also possible to create RFID gates on production lines to monitor the movement of pieces and products.

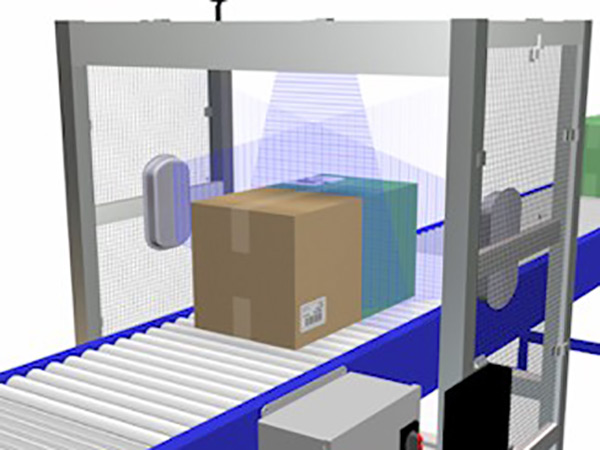
RFID AND APPLICATION SECTORS
RFID is a very widespread tool in the industrial field, let’s now analyze the following possible applications, divided by type of use:
- Traceability –> uniquely identify an entity. Follow the movements of raw materials and semi-finished products on pallets moved by forklifts or forklifts in general.
- Inventory –> in order to contain the cost of carrying out inventories. Check the presence or absence of a tool or raw material inside the cabinets and shelves.
- Product identification –> traceability of uniquely identifiable objects. Recognition and identification of the components to be machined.
- Fraud prevention –> assigns each object a unique label, not readable by unauthorized persons
- Access control –> attendance tracking connected to personnel management software.
- Shipments -> Reading of the pallets loaded on trucks through the gate.



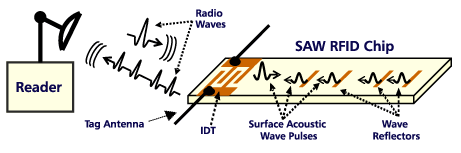
RFID SAW
SAW-based RFID systems have the inherent ability to measure tag location, direction of movement, and tag temperature; features that are expensive or difficult for standardized RFID tags to implement. In addition, SAW RFID tags can also be read through metal walls (up to a certain thickness), can withstand high operating temperatures, high energy X-rays and gamma ray sterilization.
The SAW RFID tag uses an inherently cheaper chip in combination with a smaller and less expensive tag antenna, resulting in a substantial cost advantage over traditional IC-based tags.
Main features of SAW RFID Tags:
- Overcomes many limitations of IC-based RFID chips, including power requirements and performance limitations;
- It can operate worldwide in compliance with RF industry regulations;
- It is significantly cheaper than traditional IC-based RFID chips;
- Provides a virtually unlimited number of identification codes;
- Provides a superior reading range while maintaining accurate, high-speed readings.
Operation of the SAW RFID system:
The player emits a radio wave pulse that is converted directly into a nanoscale surface acoustic wave on the surface of the SAW chip by the IDT (interdigital transducer). That acoustic wave travels past an array of wave reflectors to produce uniquely coded acoustic wave pulses, which return to the IDT. The IDT converts these pulses into an encoded radio wave response signal which is sent to the reader. The SAW chip works using the piezoelectric effect and requires no DC power.